PCB’s surface finishing
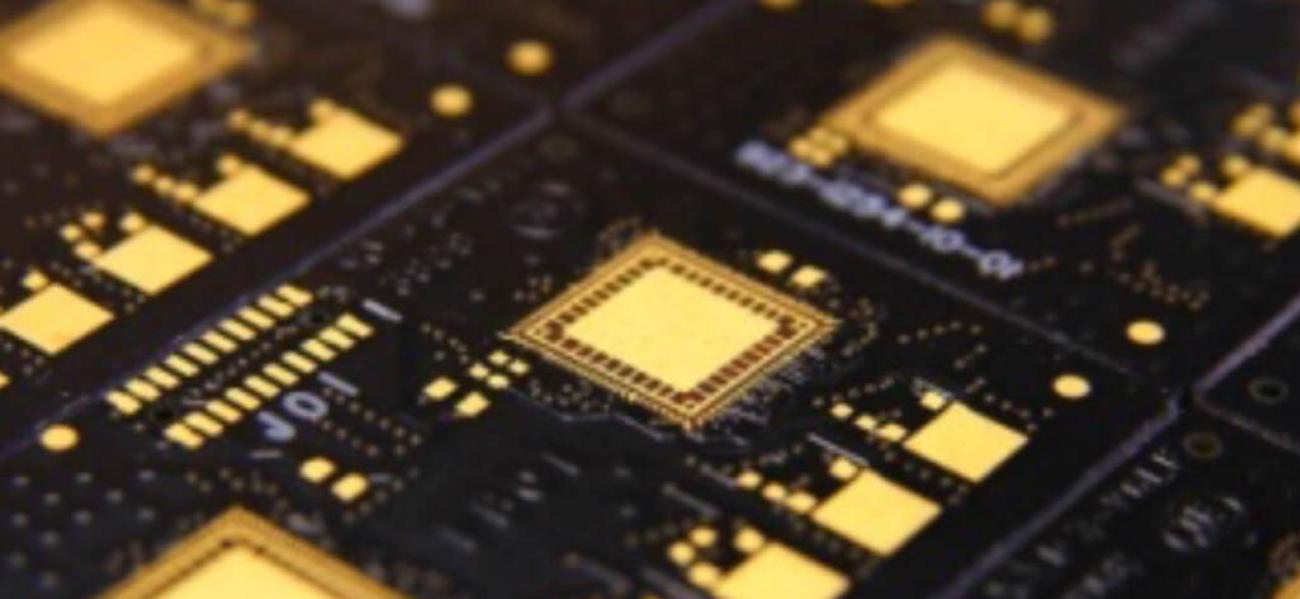
Surface finishes technologies for Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing have a crucial role in electronic components assembling. Copper surface on PCBs is exposed to oxidation with the risk to significantly reduce soldering quality. Surface finishing is necessary to prevent pads’ oxidation granting an excellent soldering and related PCB electrical performances. Finishing choice is a fundamental step for PCB production processes optimization and following assembling phases.
Since ever suggested by IPC Guidelines, it is fundamental to have a one-stop approach between those who produce the PCB and those in charge of assemby to avoid or at least to reduce risks due to design or to PCB production process.
Speaking about finishing, it is important to evaluate different perspectives related to manufacturing process and to PCB’s technological characteristics, and to following assembling operations too. It is fundamental to do a detailed product analysis to define the most suitable surface finishing. Exchange of information between the PCB manufacturer and the assembly house could prevent possible problems so to positively influence the final product quality. Knowing the kind of process adopted during the assembling (i.e. reflow, reflow in an inert atmosphere, number of soldering phases, manual soldering), can address the manufacturer of PCBs to offer different surface finishing depending on the PCB itself.

Each surface finishing have specific characteristics, which mark pros and cons and, referring to cons, right tricks and precautions can be taken during PCB manufacturing.
Among the information to take into consideration, the most important ones are:
- PCB type
If it is a rigid PCB in FR4 or it is a flex or rigid flex PCB for which HASL finishing are recommended - Presence or not of BGA (Ball Grid Array) o VFP (Very Fine Pitch) Technologies
For which chemical finishes are suggested (ENIG,ImTin,ImAg) - Assembling cycle adopted assuring a specific finishing can support it
Finishing such as chemical Tin or standard OSP are not suggested for product which request two or more soldering cycles.Assembling lead time since some finishing has limited shelf lifeFinishing such as chemical Tin, OSP or chemical Silver have a limited shelf life compared to others HASL finishing - Handling
Some finishing requires specific attention compared to others.
The most requested surface finishing are:
- HASL - Hot Air Solder Leveling - Sn/Pb
- HASL - Hot Air Solder Leveling - Lead Free
- ENIG – Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold- Chemical Gold
- IMMERSION Tin- Chemical Tin
- IMMERSION SILVER - Chemical Silver
- OSP - Organic Solderability Preservative
- HARD GOLD - Hard Gold Electrolitic
- ENIPIG – Electroless Nichel immersion Palladium immersion Gold
- HOT OIL REFLOW - Tin-Lead Hot Oil reflow
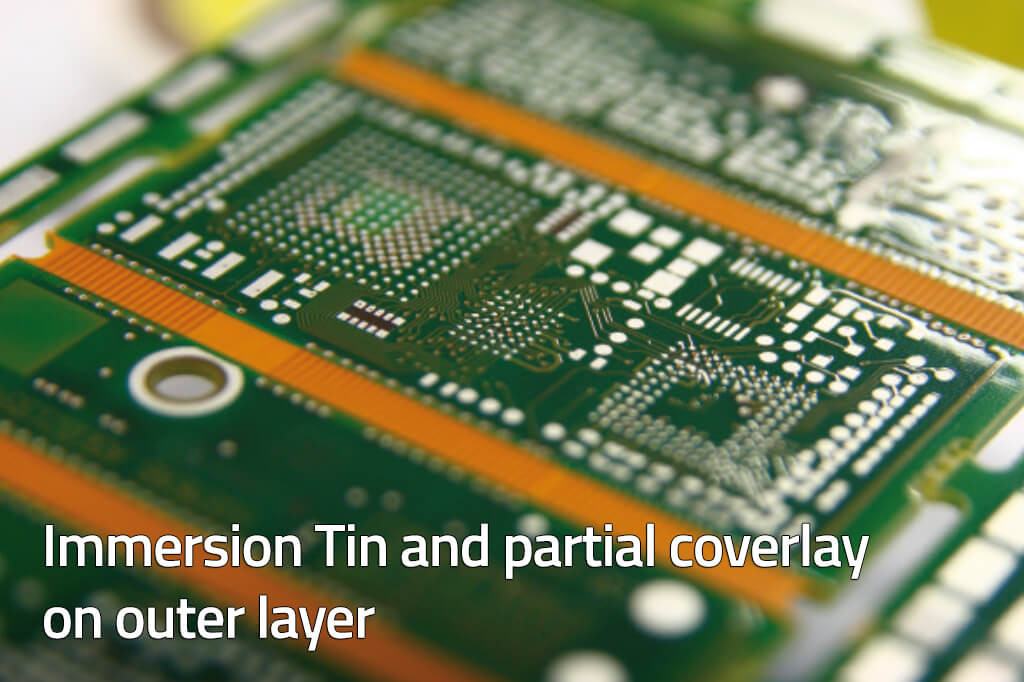
Each one of these finishing has positive and negative characteristics depending on product, on PCB’s technology and on following assembling operations.
In our next article we will explain each detail to better understand when choose each single finishing technology.